The Way of Web3.0: The evolution of Internet 3.0
The Internet is a constantly changing and evolving ecosystem, from the original Web1.0 “reading Internet” to the current Web2.0 platform-centered “reading and writing Internet”, has undergone great changes. However, with the explosive growth of data, the Internet is also facing many challenges. Web2.0 is based on the establishment of end-to-end transmission pipeline IP network as the underlying architecture, which means that users need to establish a connection with the server of the centralized platform in order to interact with others, while enjoying convenient services. They also face the risk of losing control of their data and identity, of transactions being monopolized by platforms, and of data being abused. To address these challenges, a more open, free, and fair Internet paradigm is needed, which is Internet 3.0.
What is Web3.0? Simply put, it is to let the user truly become the master of the Internet. Compared with Web2.0, Web3.0 adds the concept of ownership on the basis of “readable and writable”, emphasizing that users have autonomy over identity (ID), content, and data, and users are completely the owners of property rights in their own production activities, that is, “decentralization”. At present, Web3.0 is a new generation of value Internet based on the concept of trust, decentralization and digital asset conversion, with blockchain P2P network as the underlying technology, digital production and digital consumption as the main economic form, and will be value-centered, through the production, exchange, incentive and other mechanisms of data, to improve the mobility and value of data.
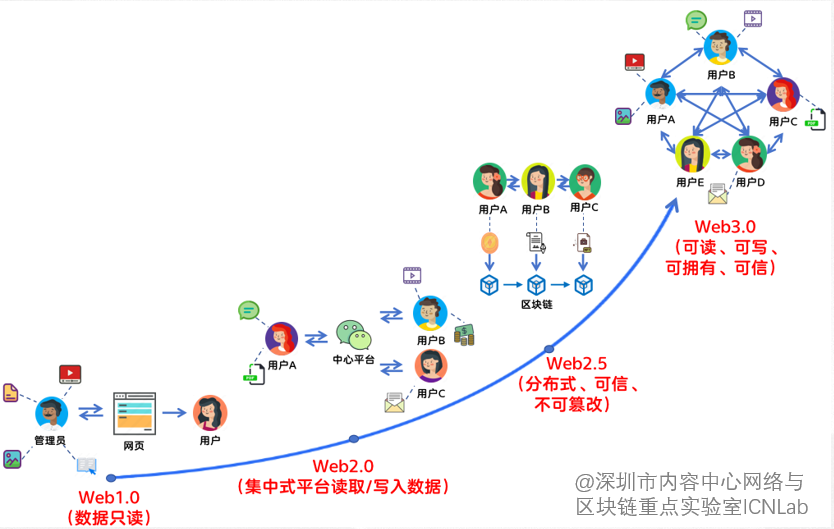
Figure 1. Evolution of the Internet
Web3.0 sounds wonderful, but from “feudal” to “republic” is not a day, Web2.0 to Web3.0 vision is not overnight, now the mainstream based on blockchain technology Web3.0 can only be seen as a “Web2.5” existence. The decentralization of data is also limited to a single blockchain, unable to achieve interoperability between chains, and does not directly solve the problem of information islands. In addition, from the current technical point of view and the underlying architecture, it is unrealistic to want to implement a pure Web3.0 immediately, and needs to consider the practical situation. This means not abandoning the existing Web2.0 system entirely, but improving, innovating, and integrating on its foundation. Web2.0 still has its advantages and necessity in some aspects, such as providing effective supervision, convenient interaction, flexible application and so on. Therefore, a gradual transition is needed to integrate the advantages of Web2.0 with the value of Web3.0 as the central feature, and gradually move towards Web3.0.
Second, the change of Web3.0: the innovation of Internet 3.0 NFT
In the future digital world of Web3.0, data will become the first element, and its form of existence is no longer a homogeneous commodity or service, but a unique, irreplaceable and verifiable digital asset. This digital asset is called a Non-Fungible Token (NFT).
Traditional single-semantic NFT has a series of limitations in its current form, which hinder its wide application and further development in Web3.0. First, single-semantic NFT must be strongly dependent on a specific blockchain network, cannot natively achieve cross-chain interoperability, and creation, verification, and transactions on different blockchains are restricted, hindering their availability and liquidity. In addition, when casting a single semantic NFT, the user needs to pay the gas fee before the value is reflected, this uncertain production model is unreasonable and may reduce the enthusiasm of users to participate. In addition, the association between a single semantic NFT and its metadata often relies on mapping, which does not guarantee the security and reliability of the asset itself.
In order to solve the problem of single-semantic NFT, and to adapt to the transition from Web2.0 to Web3.0, a new concept is needed – everything can be NFT. The idea is that any valuable data, whether it is a user’s identity, content, data, or services, functions, or computation-can become a Semantic information-rich NFT, or “Rich Semantic NFT.” Its core is to combine NFT and named addressing closely to realize unbound digital assets that can be carried across the whole network and classified, graded and subject. Unlike single-semantic NFT, rich semantic NFT does not depend on a specific blockchain, but exists in the form of a combination of “encapsulated NFT” and “unbound NFT” (patent: CN114065269B “Generation method and parsing method and storage medium for Unbound Non-homogeneous Tokens”). This means that it directly encapsulates metadata and the digital asset itself to form a separate, semantically rich, irreplaceable digital entity that can circulate freely on and off the chain, thus eliminating the limitation of cross-chain interoperability.
Rich semantic NFT can be divided into two main categories: recording NFT and functional NFT. Recording NFT is similar to the concept of traditional coin circle single semantic NFT and is used to record and identify assets. Like your ID, your student ID, or your collection of boring ape art. Functional NFT is used to provide functions and services, such as you can use a functional NFT to visit a website, use an application, perform a calculation, and so on.
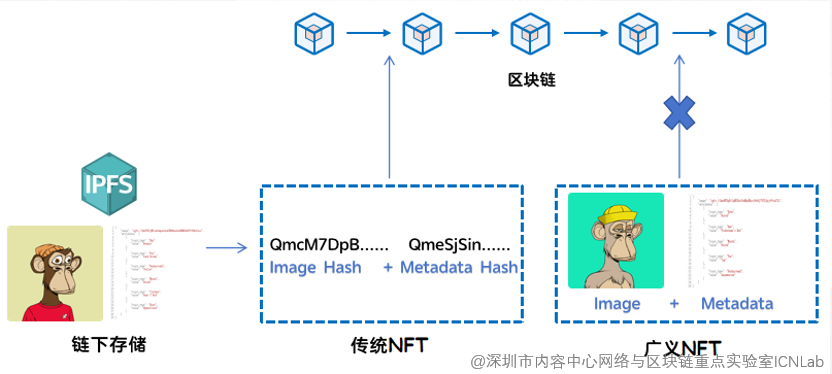
Figure 2. Transformation from single-semantic NFT to rich semantic NFT
This is an innovative NFT data mode, which breaks the limitations of traditional single-semantic NFT, provides a broader space and possibility for the future digital world, can support more application scenarios and innovative ways of use, and is expected to become an important development direction in the field of digital assets in the future.
Third, the structure of Web3.0: content-centered semantic NFT chain network integration architecture
Recently, Web3.0 has been hyped up, and a large number of applications have emerged in order to catch the heat of Web3.0. However, most of the so-called innovations for Web3.0 are just blockchain-based Web2.5, just changing the soup. Therefore, it is important to understand that blockchain is not a panacea and cannot solve all problems, but ultimately there are problems with the underlying structure of the existing network.
Today’s TCP/ IP-based Internet architecture is “overwhelmed”, it was designed by researchers 50 years ago to connect multiple heterogeneous networks, no one expected the Internet would become popular in the 1980s and 1990s, and then today’s development goal of decentralization concept, application model has produced a sea change. The defects that the underlying design of the Internet does not fit the upper application are gradually exposed, and the traditional IP architecture can only alleviate the existing problems by patching the form, and ultimately only treat the symptoms rather than the root cause. Specifically, IP has not considered the decentralized application scenario from the beginning of its birth. It has rigid Internet architecture, weak content perception ability, poor multi-architecture/multi-network integration ability, and also faces problems such as low flexibility in control scheduling and overall consideration, and lack of endogenous trust maintenance mechanism. These defects lead to the low service quality of IP protocols for upper-layer multi-type applications (such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data), and also limit the development space of decentralized applications. In contrast, the centralized application ecosystem can better highlight the advantages of the IP protocol to achieve efficient and stable services.
In order to realize the vision of the future digital world facing decentralized Web3.0, a new Internet architecture is needed to solve various problems existing in the existing architecture, and be compatible with the advantages of Web2.0, while adapting to the characteristics and requirements of Web3.0, and complete the great transformation from the establishment of pipeline communication as the center to the content itself. Form a new form of pan-centralized future Internet.
IEN (Intelligent Eco Networking) is a knowledge-driven future value Internet architecture solution. It was first proposed by “ICNLAB of Shenzhen Content Center Network and Blockchain” of Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School at the 2018 IEEE HotICN International Conference. Based on the technical route of virtualization, programmable devices and the combination of software and hardware, IEN improves the network architecture of information center, integrates distributed artificial intelligence analysis and decision and blockchain consensus computing technology, considers the cost/benefit indicators of storage, computing and bandwidth network resources, and builds a new hierarchical, intelligent and semantic advanced architecture of intelligent network.
With the goal of future-oriented network becoming more and more clear, IEN’s iterative upgrade version IEN Web3.0 came into being. Different from the past, it is not only a network layer architecture, but also a future-oriented Internet architecture, emphasizing the content-centric semantic NFT chain network, supporting the application and flow of rich semantic NFT, which covers the network layer, distribution layer and some application layer functions, and attaches importance to the collaboration and integration of the application layer and the network layer. More importantly, IEN Web3.0 does not intend to realize the real Web3.0 at the beginning, but exists in the form of Web2.8, constantly exploring and innovating, and gradually opening the door to the future Internet.
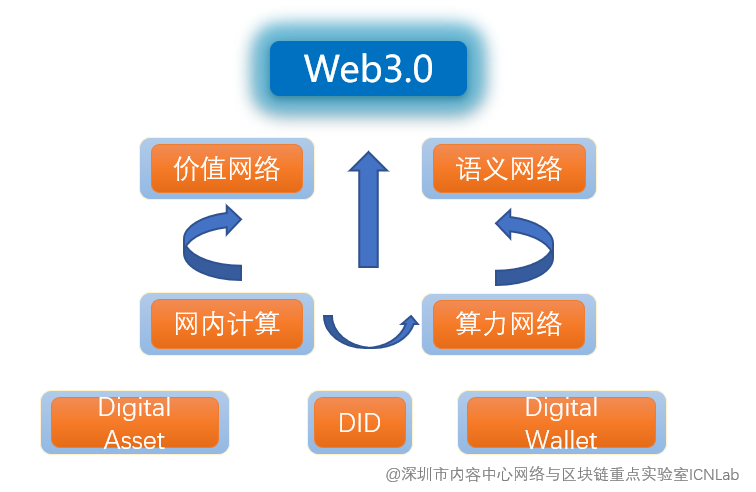
Figure 3 IEN Web3.0 network architecture
The ultimate goal of IEN Web3.0 is to form a Web3.0 oriented infrastructure for chain convergence. Academician Wang Jian believes that infrastructure has two basic characteristics, one is very easy to get, the second is cheap, if you do not meet these two conditions can not be called infrastructure. The future of a prosperous civilization requires the participation of all, and all participants should be able to participate in the construction of the digital world at low cost. IEN Web3.0’s future-oriented design makes it a key force leading the future development of the Internet, providing a more solid foundation for the sustainable development of the Internet.
The foundation of Web3.0: Semantic multi-domain flow infrastructure
In the initial state of the IEN Web3.0 digital world, a character similar to “Pangu Kaitian” is needed to create the basic content of the rules, structures, functions and resources of the entire world. “Genesis NFT” is a special functional NFT. It is a basic component associated with IEN Web3.0. It has the ability to create other semantic rich NFTS, which can be used to generate a variety of record and service NFTS, and give deeper semantic information to the NFT generated by ordinary users. Complete decentralization is not realistic, but to achieve a maximum degree of decentralization, that is, “pan-center”, so the Genesis class NFT can only be operated by users with specific permissions, so as to ensure the security and stability of the digital world.
Unlike traditional IP networks, which are mainly oriented towards establishing pipelines for ubiquitous data exchange, IEN Web3.0 focuses on the exchange centered on “valuable data”, that is, the value exchange of rich semantic NFT. To achieve this, IEN Web3.0 has designed a set of protocols based on Named Data Networking (NDN) to ensure the efficient circulation of rich semantic NFT, providing it with complete lifecycle management and ensuring the sustainable development of the IEN Web3.0 digital world.
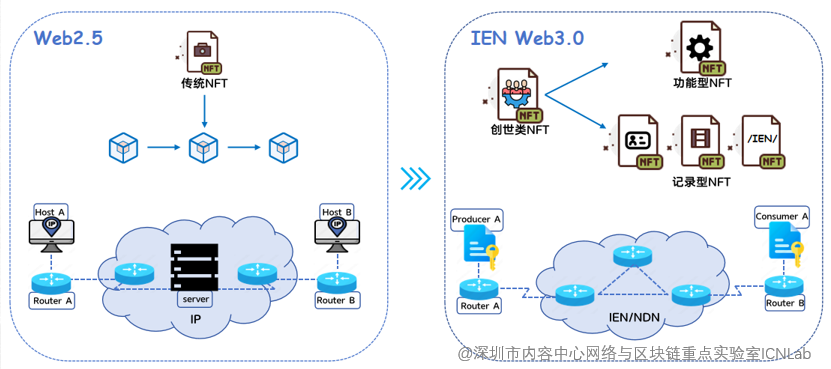
Figure 4 Semantic multi-domain flow infrastructure
Through the semantic more than flow infrastructure such as Genesis NFT and IEN Web3.0 protocol, a content-centric semantic NFT chain network is built to transform data from mere information into digital assets with value and significance, and realize the asset-based, semantic and ecological data. This new Internet architecture not only provides users with more autonomy, participation and profitability, but also opens up new space and possibilities for Internet innovation and development.
Copyright ©️ Shenzhen Content Center Key Laboratory of Network and blockchain ICNLab
© Copyright by the author: Shenzhen Computer Society original works, please contact the author for reprinting authorization, otherwise will be investigated for legal responsibility
