
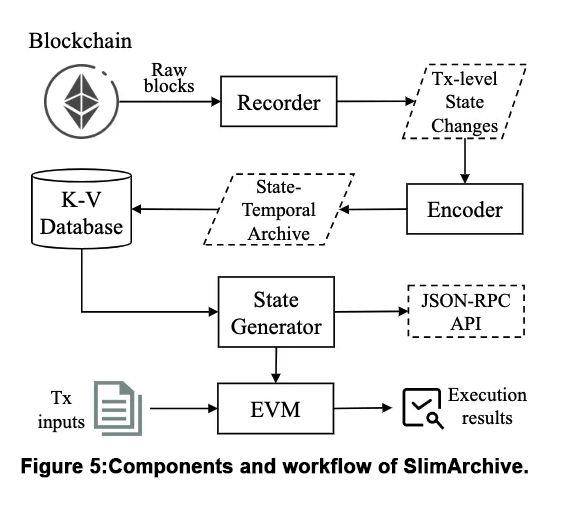
The rapid growth of Ethereum necessitates robust archive nodes that capture all historical states, yet current models struggle with immense storage needs and subpar performance due to inefficient authenticated Merkle Patricia Tries and coarse state granularity. This paper introduces SlimArchive, a novel lightweight and high-performance architecture for Ethereum archive nodes, designed to overcome these challenges. The core innovation lies in preserving compact, flattened, transaction-level historical states by recording minimal state changes for each transaction. This approach drastically reduces storage demands while significantly enhancing state access performance. Our prototype, SLIMARCHIVE, demonstrates remarkable efficiency, reducing storage requirements by 98.1%, increasing state access throughput by 19.0×, and accelerating transaction execution by an average of 1112.5× compared to vanilla Geth.
随着以太坊的快速发展,记录所有历史状态的存档节点成为基础设施的重要组成部分。然而,由于认证的 Merkle Patricia Trie 效率低下和状态粒度粗,当前的存档节点面临着巨大的存储需求和较差的性能表现。本文提出了一种新颖的轻量级、高性能的以太坊存档节点架构SlimArchive,以解决这些问题。其核心创新在于通过记录每笔交易的最小状态变化来维护紧凑、扁平的交易级历史状态。这一方法显著减少了存储需求,同时大幅提升了状态访问性能。我们实现的原型系统SLIMARCHIVE展示了出色的效率,相较于vanilla Geth,存储需求减少了98.1%,状态访问吞吐量提高了19.0倍,交易执行速度平均提升了1112.5倍。
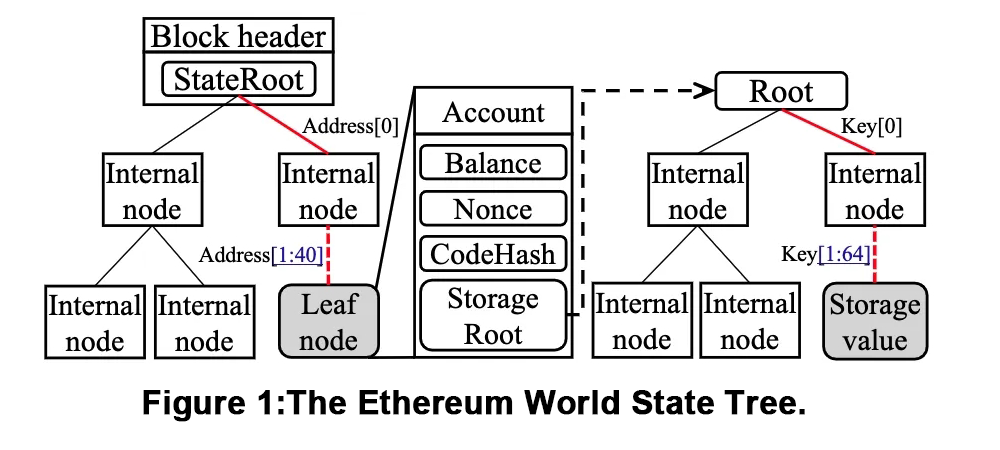
如图1所示,以太坊维护两种类型的MPT:状态Trie(左侧部分)和存储Trie(右侧部分)。每个区块记录账户状态的StateRoot;每个合约账户记录合约存储状态的StorageRoot。账户和存储数据存储在叶节点中(图1中的灰色矩形)。MPT是一个16基数Trie,路径由一系列十六进制数字表示地址或插槽密钥。为了节省磁盘空间,如果节点只有一个子节点,MPT会将节点与其子节点合并。因此,MPT的实际深度低于完整的MPT。在以太坊中,状态访问需要从根到叶搜索MPT(图1中的红线)。
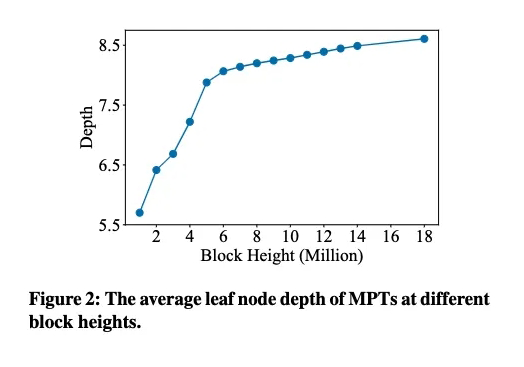
1: 在大多数实际使用场景中,不需要对历史状态进行数据认证。
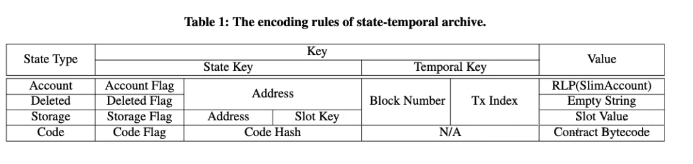
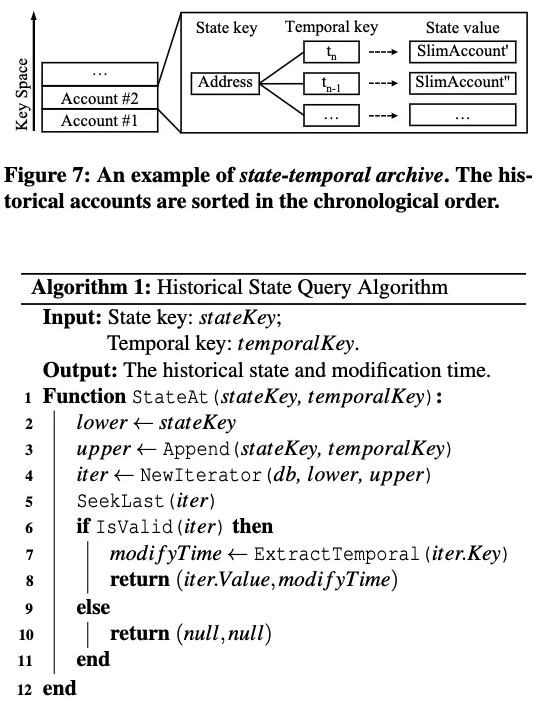
解决方案: 为了在不需要数据认证的情况下实现更高效、更具成本效益的存档节点,我们采用压缩扁平的数据模型,而不是复杂的历史状态MPT,以最大限度地减少中间数据并简化状态访问。
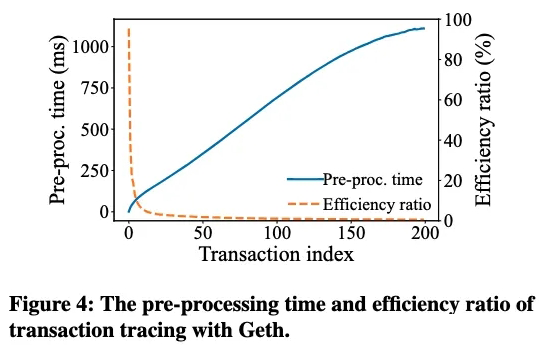
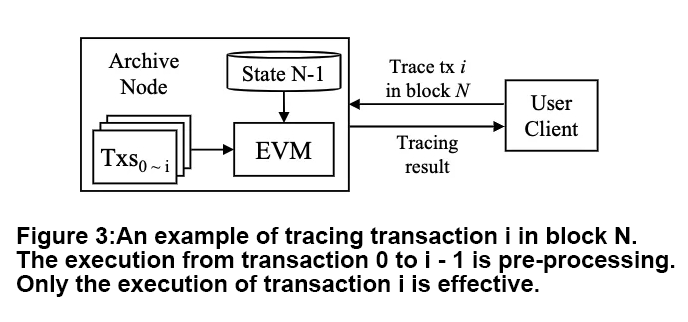
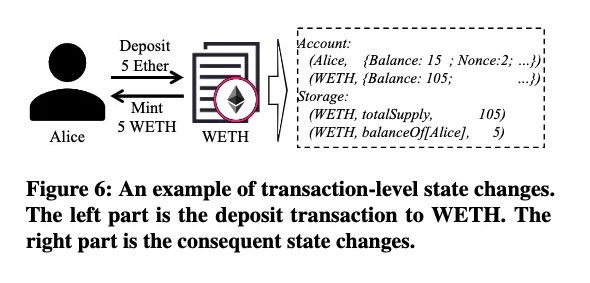
2: 虽然以太坊在外部看起来具有块级状态转换,但在低级执行层(EVM),导致状态转换的基本单位是交易,即执行层状态转换的粒度是交易。
解决方案: 我们可以将历史状态的粒度细化为执行层的交易,以消除预处理造成的开销。
Pdf link:
https://www.usenix.org/conference/atc24/presentation/feng-hang
文章来源:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fOqqrYUtv7QqDn9e0Gzlew
